Table of Contents
- Effortless Goods and Services Classification: Instantly Categorize with AI
- How Classifast Works: Semantic Search and High Performance
- Practical Use Cases: Who Benefits from Automated Classification?
- Step-by-Step Guide: Using the Online Goods and Services Classifier
- Frequently Asked Questions: Goods and Services Classification Explained
- Unlock Consistent, Accurate Classification with Classifast
Effortless Goods and Services Classification: Instantly Categorize with AI
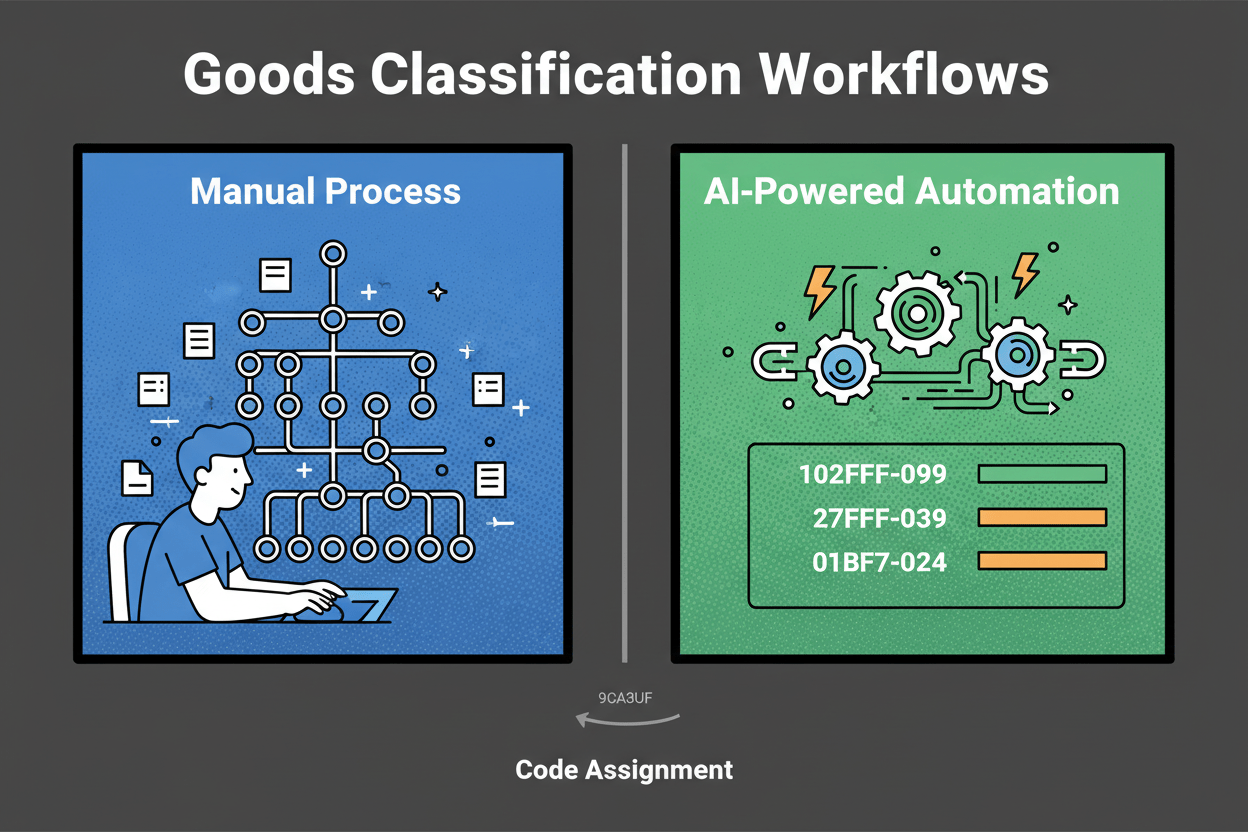
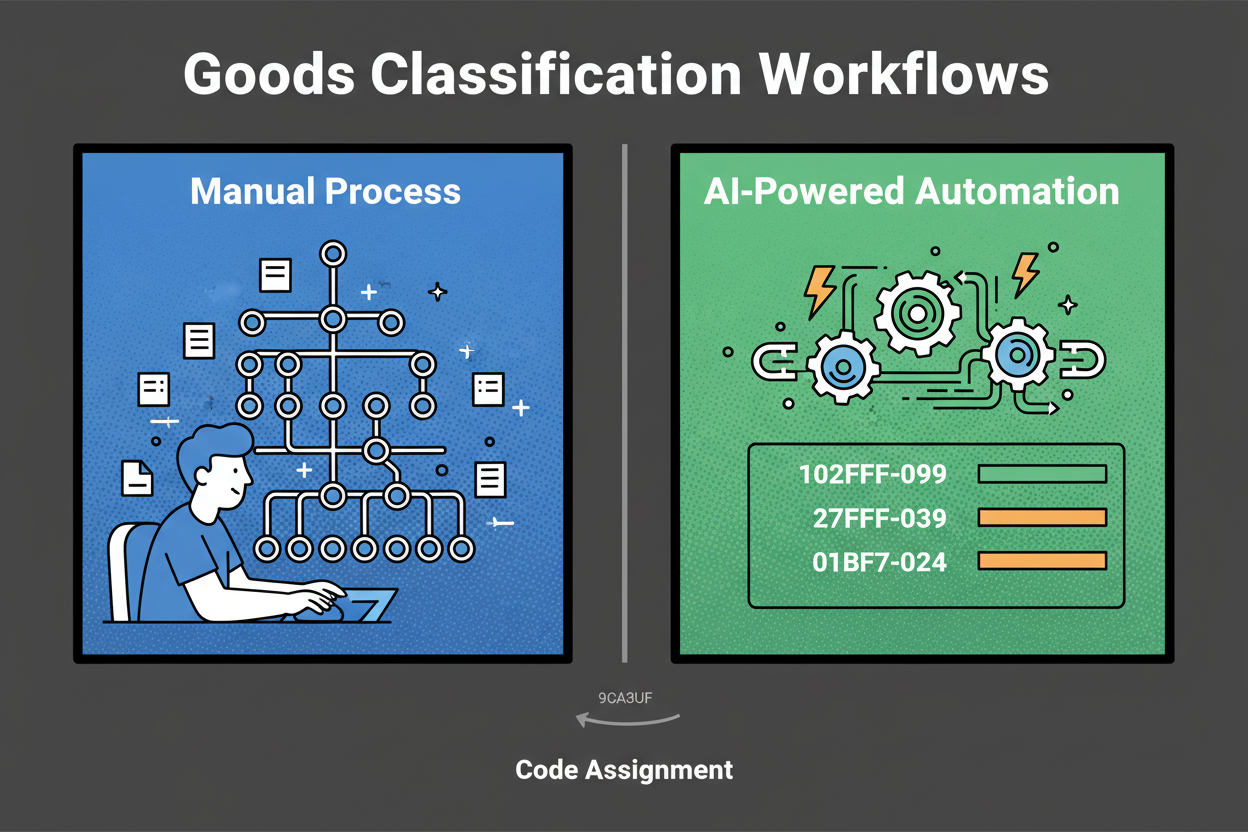
You’re staring at a spreadsheet with hundreds of items. A few are simple. Most are oddly specific or bundled. You tab between a category tree, a customs reference, and a marketplace guide. Each choice feels like a guess you’ll have to defend later. Goods and services classifier is required.
That’s the grind of manual classification. It’s slow, inconsistent, and it doesn’t scale. In catalog operations, humans typically spend 30–180 seconds per SKU just to pick a product category. Assigning an HS code for a trade can take 5–20 minutes per line when you check notes and rulings.
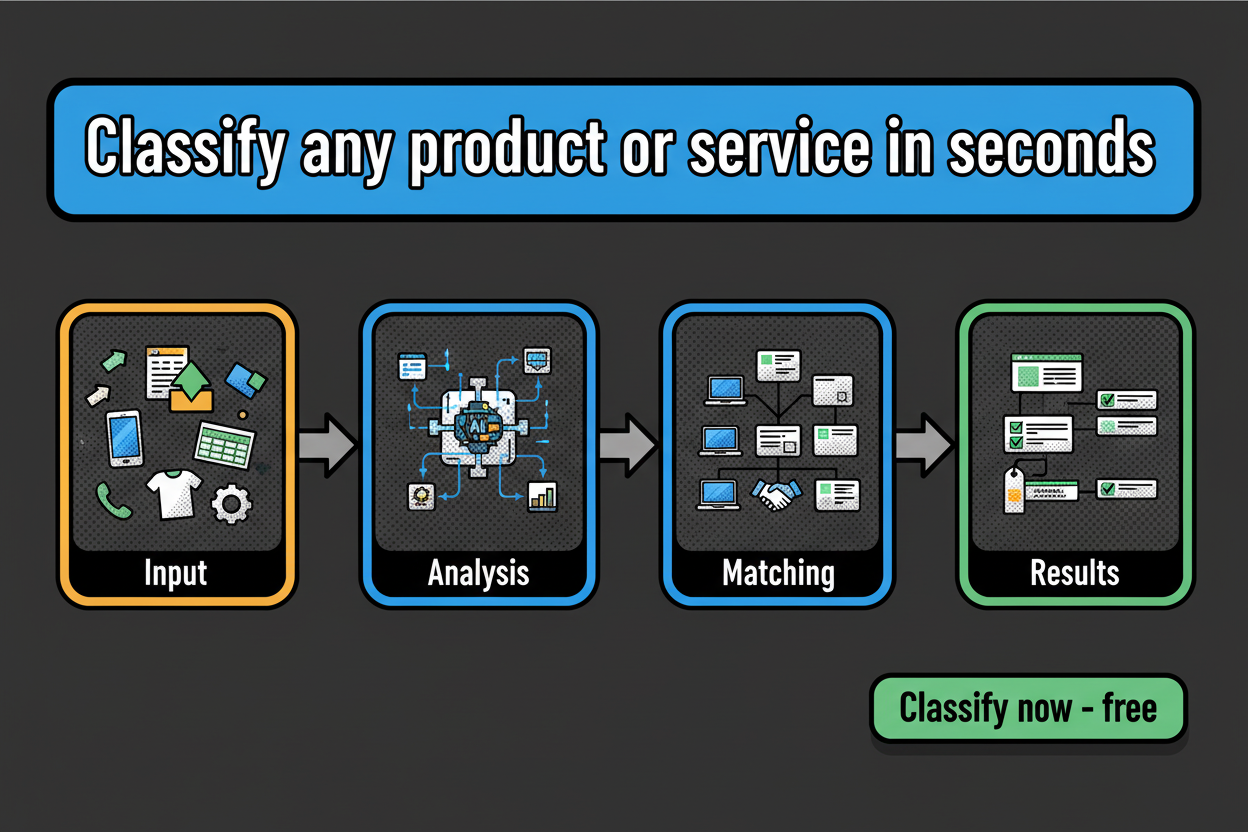
What if you could paste a description, click once, and get the best-fit code with a confidence score and a short rationale? That’s exactly what Classifast does. Classifast is a web application designed for the instant classification of goods and services using advanced semantic search technology to ensure accuracy and speed.
What is a goods and services classifier?
A goods and services classifier reads a product or service description and assigns the right code from a defined taxonomy. Classifast supports major international standards, including:
- UNSPSC (Procurement and spend analytics)
- NAICS (Industry classification)
- ISIC (International standard industrial classification)
- HS/HTS (Global trade and customs)
- ETIM (Electrotechnical and technical product data)
The benefit is simple: consistent labels for compliance, analytics, and findability, generated instantly with transparent confidence measures.
How Classifast Works: Semantic Search and High Performance
You shouldn’t have to guess how an AI made its pick. Classifast is built with modern web technologies like FastAPI to deliver near-instant results. Unlike traditional keyword matching, our system uses advanced semantic search. This means the tool understands the context and meaning behind your text, not just the words themselves.
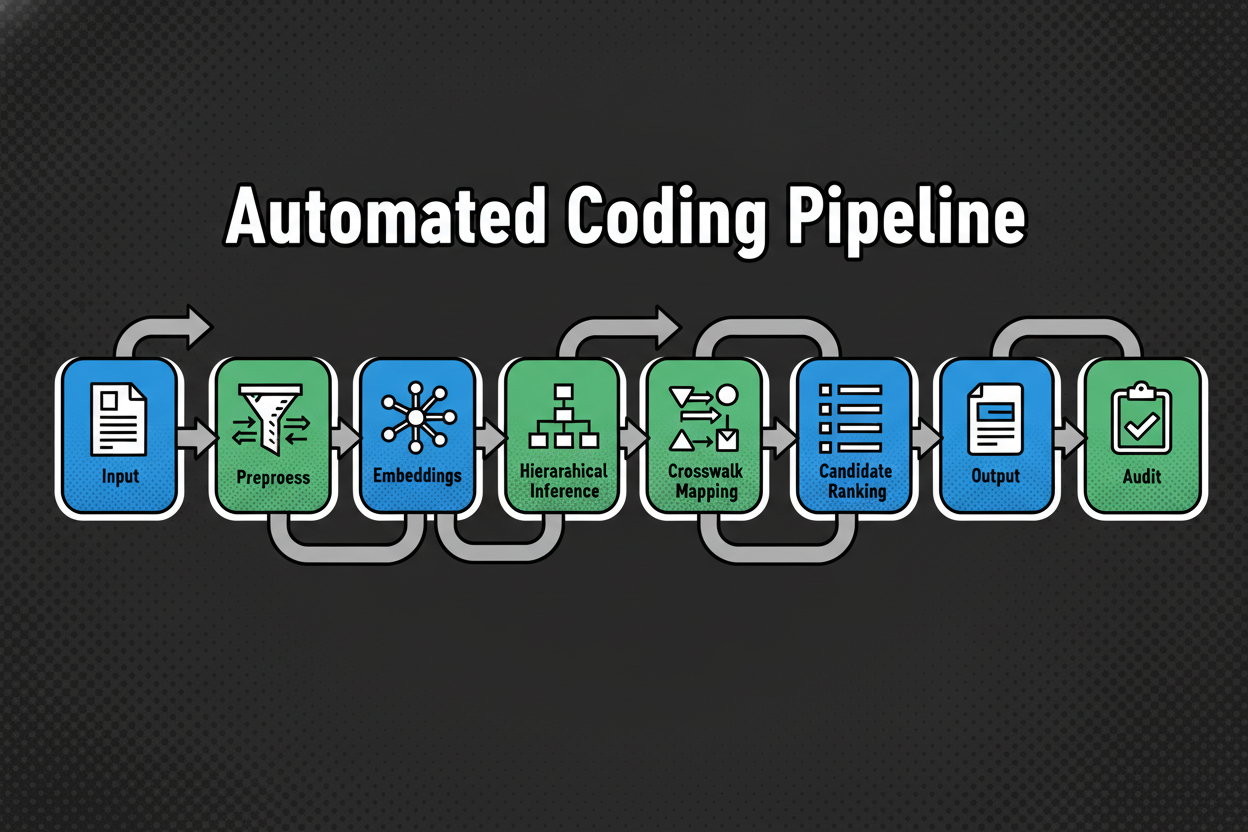
The AI Pipeline: From Description to Code
- Inputs: You provide a title, description, or attributes (like materials or voltage).
- Preprocessing: Classifast cleans the text, detects the language, and prepares it for analysis.
- Semantic Embedding: The text is converted into high-dimensional vectors that capture its true meaning.
- Hierarchical Inference: The model drills down the taxonomy (e.g., from “Electronics” to “Smartphones”) to find the exact leaf node.
- Output: You receive a top code, a confidence bar, and a rationale explaining the decision.
Practical Use Cases: Who Benefits from Automated Classification?
Automation is useful when it moves needles: faster cycles, cleaner data, and fewer rework loops.
- Compliance Officers: Reduce HS/HTS research time and keep audit-ready logs for every shipment.
- Ecommerce Managers: Stabilize categories across your site to improve findability and reduce returns.
- Procurement Leads: Map thousands of PO lines to UNSPSC instantly to unlock true spend visibility.
- Data Scientists: Ensure consistent labeling across datasets to build better forecasting models.
Step-by-Step Guide: Using Classifast
Getting started is simple. You don’t need a complex integration to begin cleaning your data today.
- Prepare your data: Use clear, factual titles and descriptions. Include specs like materials or intended use.
- Choose your taxonomy: Select from UNSPSC, NAICS, ISIC, ETIM, or HS.
- Run the classification: Click “Classify” and get results in seconds.
- Review and Audit: Check the confidence score. If it’s high, you’re good to go. If it’s low, the rationale will tell you what extra info (like “material type”) is needed to be certain.

Bulk Classification for Large Projects
For those with tens of thousands of SKUs, Classifast supports bulk uploads. Upload your CSV, map the columns, and let the semantic engine process the entire batch. You can set a “confidence threshold” to automatically accept the most certain results, leaving only the edge cases for human review.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Which systems does Classifast support?
A: We support UNSPSC, NAICS, ISIC, ETIM, HS/HTS, GS1 GPC, and eCl@ss. We can also map to your own custom internal taxonomies.
Q: How accurate is the semantic search?
A: Semantic search allows Classifast to understand synonyms and technical context that traditional tools miss. This often matches or exceeds human accuracy in complex retail or industrial settings.
Q: Is my data secure?
A: Yes. Classifast practices data minimization and uses encryption in transit and at rest. We align with SOC 2 and ISO 27001 principles to ensure your product data is protected.
Unlock Consistent, Accurate Classification with Classifast
The real win of moving to an automated system is simple: faster outputs, steadier decisions, and clean data you can trust. Manual labeling is a bottleneck that your business can’t afford in 2025.
By using Classifast.com, you shift from minutes per item to seconds. You invest human time only where it moves the needle—on high-risk exceptions—while the semantic engine handles the rest.
Key Takeaways
- Instant Results: Categorize in seconds using FastAPI-powered search.
- Global Standards: One tool for UNSPSC, NAICS, ISIC, HS, and ETIM.
- Defensible Logic: Every code comes with a rationale you can audit.
- Consistent Data: Eliminate the variance caused by human error and manual fatigue.
Ready to try it? Visit Classifast.com to run your first items right now. No sign-up required—just paste your description and go.